How Does a Slew Ring Work?
2024-07-30
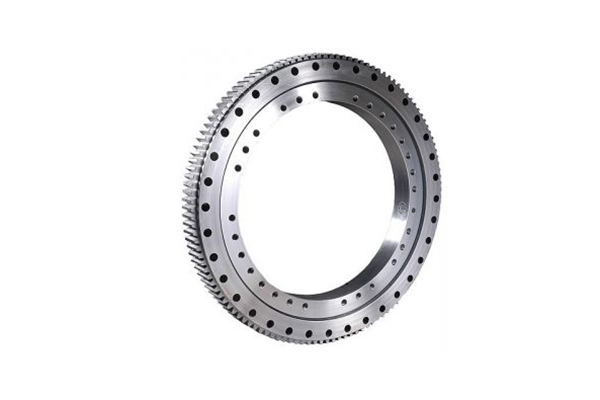
A slewing ring, also known as a slewing bearing or turntable bearing, is a crucial component in many types of heavy machinery and equipment, facilitating rotational movement and supporting axial, radial, and moment loads. Understanding how a slew ring works involves looking at its design, components, and applications.
Design and Components
A slew ring consists of several key parts:
- Inner and Outer Rings: These rings are the primary structural components. One ring is usually fixed to a stationary part of the equipment, while the other rotates.
- Rolling Elements: Between the inner and outer rings are rolling elements, which can be balls or cylindrical rollers. These elements reduce friction and allow for smooth rotation.
- Raceways: The inner surfaces of the rings where the rolling elements move. These raceways are precision-machined to ensure smooth and efficient movement.
- Seals: Protective seals are used to keep out dirt, debris, and moisture, which can cause wear and tear.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is crucial to reduce friction and prevent wear, ensuring the longevity and efficient operation of the slew ring.
- Gear Teeth: Some slew rings include gear teeth on the inner or outer ring, which are used to transmit rotational force. These are known as geared slewing rings and are driven by a pinion or other gear system.
Working Mechanism
The basic working principle of a slew ring is relatively straightforward. The rolling elements, typically balls or rollers, are arranged between the inner and outer rings, allowing one ring to rotate smoothly relative to the other. This rotational movement is facilitated with minimal friction due to the rolling elements. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- Load Distribution: The slew ring supports axial, radial, and moment loads. Axial loads are parallel to the axis of rotation, radial loads are perpendicular, and moment loads are tilting forces.
- Rotation: When a rotational force is applied, the rolling elements move along the raceways. This movement allows the inner ring (attached to the rotating part of the machinery) to turn relative to the outer ring (attached to the stationary part).
- Transmission of Force: In the case of a geared slewing ring, gear teeth on the ring engage with a pinion or gear system. This engagement transmits the rotational force, causing the ring to turn. The precision of the gear teeth and the engagement with the pinion ensure smooth and controlled rotation.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Continuous lubrication reduces friction and wear. Maintenance involves regularly checking and replacing lubrication, inspecting seals, and ensuring that the rolling elements and raceways are in good condition.
Applications
Slew rings are used in a variety of applications due to their ability to support heavy loads and provide smooth rotational movement:
- Cranes: In cranes, slew rings allow the boom to rotate horizontally, facilitating the lifting and positioning of loads.
- Excavators: They enable the upper structure of an excavator to rotate, providing the necessary maneuverability for digging and moving materials.
- Wind Turbines: Slew rings in wind turbines allow the nacelle to rotate, ensuring that the blades are always facing the wind for maximum efficiency.
- Aerial Platforms: They provide the rotational movement needed to position the platform accurately.
Advantages
- High Load Capacity: Slew rings can support substantial axial, radial, and moment loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Smooth Operation: The rolling elements provide smooth and efficient rotation with minimal friction.
- Versatility: They are used in a wide range of machinery and equipment, from construction and mining to renewable energy and manufacturing.
Conclusion
Slew rings are indispensable in many industries, providing the critical function of enabling smooth and controlled rotational movement while supporting heavy loads. Their design, which includes inner and outer rings, rolling elements, raceways, seals, and lubrication, ensures efficient operation and durability. Geared slewing rings, in particular, highlight the importance of precision engineering in transmitting rotational force. Understanding how these components work helps in appreciating their value in modern machinery and industrial applications.