The Ultimate Guide to Slewing Ring Bearings: How Precision Ring Work Reduces Friction in Heavy Machinery
2025-07-08
Welcome. My name is Allen, and as someone who has dedicated their career to the design and manufacturing of slewing ring bearings here in China, I’ve seen firsthand how crucial these components are to the performance of modern machinery. If you’re a procurement officer, an engineer, or a business owner like Mark Thompson in the USA, you know that the right bearing isn’t just a part—it’s the pivot point for your equipment’s reliability and efficiency. This article is for you. We will dive deep into the world of the slewing ring, exploring how precision engineering helps reduce friction and ensures your machinery operates flawlessly. You’ll learn what to look for, what to avoid, and how to choose a component that delivers both quality and value, safeguarding your production schedules and reputation.
What Exactly is a Slewing Ring Bearing and Why is it Crucial?
At its core, a slewing ring bearing is a large-diameter rotational rolling element bearing designed to handle complex loads. Think of it as the unsung hero in a vast array of heavy machinery, from a towering crane on a construction site to a life-saving MRI machine in a hospital. Structurally, it consists of two concentric rings—an inner ring and an outer ring. Between these rings lie balls or rollers that facilitate movement, allowing one ring to rotate smoothly relative to the other. The use of slewing components is what enables a massive excavator arm to swing with grace or wind turbines to turn and face the wind.
These specialized ring bearings are designed to simultaneously manage axial (vertical), radial (horizontal), and moment (tilting) loads. This capability makes a single slewing ring a powerful replacement for more complex multi-bearing arrangements, saving space, weight, and assembly time. The slewing ring also often includes a gear, either on the internal or external diameter of one of the rings, which meshes with a pinion to drive the rotation. This integrated gear is vital for power transmission in many applications. In essence, slewing bearings are essential for any application requiring smooth and controlled rotation under a heavy load, making them a cornerstone of modern industrial machinery. The slewing ring bearing is a testament to brilliant engineering.
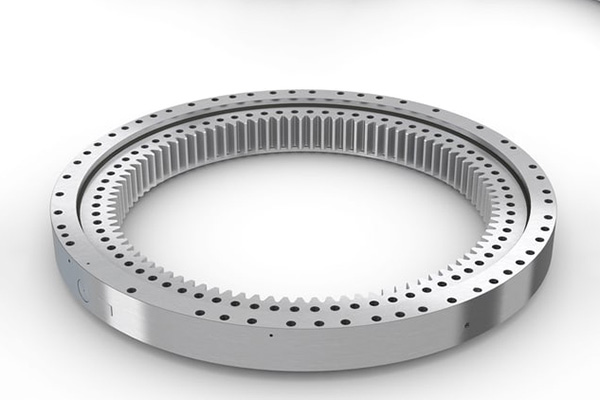

How Does Bearing Design Impact the Efficiency of Slewing Ring Work?
The bearing design is the blueprint for its performance. The geometry of the raceways—the hardened paths on the inner and outer ring where the rolling elements travel—is meticulously engineered to distribute loads evenly and minimise friction. A well-designed slewing ring will have a low coefficient of friction, which translates directly into lower energy consumption and less heat generation during operation. This is critical for the efficiency of slewing operations, especially in continuous-duty applications like wind turbines or bottling plants. Every aspect, from the raceway curvature to the material’s surface finish, contributes to the overall performance of the bearing.
Furthermore, the design of the slewing mechanism, including the type and arrangement of the rolling element, dictates the bearing’s capabilities. For example, the contact points between the rolling element and the raceways are different for ball bearings versus roller bearings. This seemingly small detail has a massive impact on the bearing’s ability to handle different load types. A superior bearing design also incorporates an effective seal system. The seal is designed to keep vital lubrication in and harmful contaminants out, which is paramount for achieving a long service life. The entire slewing ring work philosophy centers on achieving fluid rotational movement with maximum load support and minimal resistance.
What Are the Main Types of Slewing Ring Bearings and Their Applications?
Understanding the different types of slewing bearings is key to selecting the right component for your specific machinery. Each design offers a unique balance of load capacity, rigidity, speed, and precision. The choice depends entirely on the demands of the application. As a manufacturer, we produce a wide range of these bearings to meet diverse industry needs. The versatility of the slewing ring bearing is one of its greatest strengths.
Here is a breakdown of the four most common types:
| Bearing Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Row Four-Point Contact Ball Slewing Ring | Most common and versatile type. Handles axial, radial, and moment loads. Best for light to medium-duty applications. | Cranes, excavators, aerial work platforms, light industrial turntables. |
| Single-Row Crossed Roller Bearing | Features cylindrical rollers arranged in a crisscross pattern. Offers higher rigidity and precision than a ball slewing ring. | Medical equipment (CT scanners), robotics, radar systems, machine tools. |
| Double-Row Ball Slewing Ring | Uses two rows of ball bearings to provide a higher load capacity than a single-row design. Ideal for applications requiring greater stability. | Medium-duty cranes, forestry equipment, large-diameter turntables. |
| Three-Row Roller Bearing | The heavy-duty champion. Uses three independent rows of rollers to handle extreme axial and radial loads separately. | Bucket-wheel excavators, offshore cranes, large wind turbines, heavy-duty port machinery. |
The applications of slewing bearings are vast. From the immense forces managed by a three-row roller slewing bearing for bucket-wheel excavators to the fine precision required in medical devices, there is a slewing bearing for the job.
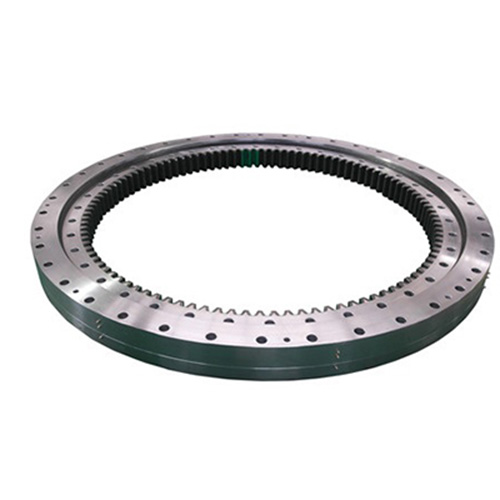

How Do Roller Bearings and Ball Bearings Differ in a Slewing Ring?
The primary difference between using balls or rollers as the rolling element in a slewing bearing lies in how they make contact with the raceways. Ball bearings make point contact. This allows for higher rotational speeds and lower friction, making a ball slewing bearing an excellent choice for applications where speed and smooth rotation are prioritized over massive load-bearing. This category includes the widely used angular contact ball bearings, which can be arranged in various ways to handle combined loads. A ball slewing ring is a workhorse in many industries.
On the other hand, roller bearings make line contact with the raceways. This greater contact area allows them to distribute loads over a larger surface, giving them a significantly higher load capacity compared to ball bearings of the same size. This makes roller bearings the go-to solution for heavy machinery and applications involving a very heavy load. However, this line contact can also result in slightly higher friction. The choice between a ball slewing design and a roller-based slewing ring is a fundamental engineering decision based on the operational requirements of the machinery.
Why is Precision So Important in Bearing Manufacturing?
In the world of slewing ring bearings, precision is not a luxury; it’s a necessity. Precision in bearing manufacturing refers to maintaining tight dimensional tolerances, ensuring the geometric accuracy of the raceways, and producing a high-quality gear. For procurement officers like Mark, verifying this is a key concern. A lack of precision can lead to uneven load distribution, increased vibration, and premature bearing failure, causing costly downtime for the end-user. Stability and precision are what separate a high-performance slewing ring from a liability.
When a slewing ring has a gear, the precision of the toothed rings is equally important. Inaccuracies in the gear profile, pitch, or backlash can lead to noisy operation, excessive wear, and inefficient power transmission. As a factory, our quality control process involves multiple checks at every stage, from raw material inspection to final assembly, to guarantee that every slewing bearing leaving our facility meets the specified standards for dimensional and rotational accuracy. This commitment to precision is what ensures the durability and reliability of the final bearing. High-quality bearing manufacturing is non-negotiable.
What Role Does Lubrication Play in the Service Life of a Slewing Ring?
Lubrication is the lifeblood of any slewing ring. Its role extends far beyond simply making things spin. A proper lubricant creates a microscopic film between the rolling element and the raceways, which is critical to reduce friction and wear. This film prevents metal-to-metal contact, which would otherwise quickly lead to surface damage and bearing failure. We’ve seen cases where proper lubrication protocols have extended the service life of a slewing bearing by more than 50%.
The functions of lubrication in a slewing ring bearing are threefold:
- Reduce Friction: The primary role is to reduce friction, which minimizes heat generation and energy loss.
- Prevent Corrosion: The lubricant coats all internal surfaces, protecting the high-grade steel from moisture and other corrosive agents that might get past the seal.
- Contaminant Flushing: During re-lubrication, the fresh grease helps to purge old, degraded lubricant and any small contaminant particles from the bearing system.
Selecting the right lubricant (typically an EP2 grease) and adhering to a strict re-lubrication schedule is essential. The seal on the slewing ring is designed to retain this grease, but it’s the consistent maintenance that truly ensures the bearing reaches its maximum operational lifespan. The role of lubrication cannot be overstated.
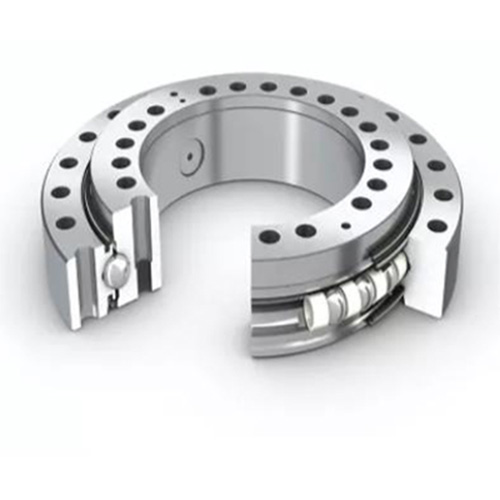

How Can You Ensure Proper Mounting of a Slewing Bearing?
A slewing ring is only as good as the structure it’s mounted on. Improper mounting is one of the most common causes of premature bearing failure. Even the highest precision slewing bearing will perform poorly if it is bolted to an uneven or flexible surface. The mounting surfaces on both the stationary and rotating structures must be perfectly flat, rigid, and clean to ensure the bearing is not distorted when the bolts are tightened.
Here are the critical steps for a successful mounting procedure:
- Surface Preparation: Ensure the mounting surfaces are machined to the specified flatness and are free of any burrs, paint, or debris.
- Bolt Quality: Always use new, high-strength bolts (Class 10.9 or equivalent) and hardened flat washers.
- Lifting and Positioning: Handle the slewing ring bearing with care, using the designated lifting points. Never lift it by its gear or seal.
- Bolt Tightening: This is crucial. Tighten the bolts in a star or crisscross pattern to the specified torque. This should be done in three stages: 30% torque, 70% torque, and finally 100% torque. This ensures the bearing seats evenly without distortion. Check the torque again after the first few hours of operation.
- Gear Backlash: For a geared slewing ring, set the proper backlash between the bearing gear and the drive pinion. This should be checked at several points around the 360-degree rotation to find the tightest point. The mounting holes are manufactured with precision to facilitate this process.
Following these mounting guidelines is essential to prevent issues with your slewing bearing. The inner and outer ring must be supported correctly.
What are the Common Causes of Wear and Tear in Slew Rings?
Even the most robust slew rings are subject to wear and tear over their operational life. Understanding the common causes can help you implement preventative measures. The primary culprits are often related to the "big three": contamination, improper lubrication, and overloading. A slewing ring bearing will show signs of distress if not cared for.
First, contamination is a major enemy. Dust, dirt, moisture, and chemical particles can get past a damaged seal and enter the bearing. These abrasive particles mix with the lubricant, forming a grinding paste that rapidly damages the raceways and rolling element surfaces. This is why the integrity of the seal is so important. Second, poor lubrication—using the wrong type, not enough, or not re-lubricating frequently enough—leads to increased friction, heat, and eventually, metal fatigue and spalling. Third, operating the bearing beyond its specified load capacity can cause permanent indentation in the raceways (brinelling) and lead to catastrophic failure. These slewing ring bearings may look tough, but they are precision instruments. Regular inspections can help reduce the wear and catch problems early.
How Do Slewing Ring Bearings Handle a Heavy Load with Low Friction?
The ability of a slewing ring bearing to handle heavy loads with low friction seems almost magical, but it’s a result of clever physics and material science. The magic lies in the use of rolling elements—the balls or rollers. Instead of two surfaces sliding against each other (high friction), the load is transferred through elements that roll. This fundamentally changes the nature of the resistance from sliding friction to rolling friction, which is significantly lower. This is the core principle that allows for the easy movement of heavy loads.
The bearing is designed to manage complex load combinations. For example, a three-row slewing ring uses one set of rollers for radial loads, another for axial loads, and a third to handle the moment load. By separating these forces and directing them through dedicated rolling paths, the slewing ring can manage immense stress while allowing the structure to rotate with minimal effort. The materials used, typically high-grade 50Mn or 42CrMo steel, are hardened to withstand the intense contact pressures without deforming. This combination of intelligent bearing geometry, the rolling principle, and robust materials is how a slewing ring achieves the remarkable feat of enabling the rotation of heavy structures with incredible ease. A powerful slewing bearing makes it all possible.

What Should You Look for When Choosing a Slewing Ring Bearing Supplier?
As a procurement officer, your choice of supplier is as critical as the bearing itself. You need a partner, not just a vendor. Based on my years of experience exporting our high quality slewing ring bearings to clients in North America and Europe, I know what discerning buyers value. They look for transparency, reliability, and expertise. Communication issues and shipment delays are common pain points that a good supplier works proactively to eliminate.
When evaluating a supplier, especially one overseas, consider these factors:
- Technical Expertise: Can they understand your technical drawings and requirements? Do they have engineers who can provide support and recommend the right slewing bearing for your machinery? Can they provide customization like this precision double-row ball slewing ring?
- Quality Certifications: Ask for material certifications for the steel used in the inner and outer ring and quality control reports for the finished bearing. Do they comply with international standards like ISO 9001?
- Proven Track Record: Do they have case studies or references from clients in your industry or country? Experience with renewable energy projects like wind turbines or heavy machinery like a crane or excavator is a good sign.
- Clear Communication: Are their sales and support staff responsive and fluent in your language? Clear, efficient communication is the key to avoiding misunderstandings and delays.
- Transparent Lead Times: A reliable supplier will give you a realistic production and shipping schedule and keep you updated throughout the process.
"As a factory owner, my reputation is built into every slewing ring bearing we ship. We are not just selling a part; we are selling the promise of performance and reliability. A good partnership is based on trust, and that trust is earned through consistent quality and open communication." – Allen, Xinda Slewing Bearing
Ultimately, a great supplier is one who understands your business goals and works with you to achieve them. They see your success as their success. The bearing is just the start.
In Summary: Key Takeaways
Choosing and maintaining the right slewing ring bearing is a critical task that directly impacts your equipment’s performance and longevity. Slewing rings play a vital role. Here are the most important points to remember from our discussion:
- Function: A slewing ring is a large-diameter bearing designed to handle combined axial, radial, and moment loads, often featuring an integrated gear for transmission of rotational force.
- Types: The four main types of bearings are single-row ball, double-row ball, single-row crossed roller, and three-row roller. The choice depends on the specific load, speed, and precision requirements.
- Precision Matters: High precision in bearing manufacturing ensures even load distribution, low vibration, and a long service life. This applies to both the raceways and the gear.
- Lubrication is Life: Proper and regular lubrication is essential to reduce friction, prevent corrosion, and flush out contaminants. It is the single most important maintenance task.
- Mounting is Crucial: The slewing bearing must be mounted on a rigid, flat surface using the correct bolt-tightening procedure to avoid distortion and premature failure. The inner and outer ring require solid support.
- Supplier Partnership: Choose a supplier who offers technical expertise, transparent communication, and verified quality. A good partner will help you avoid common pain points and ensure you get the best slewing ring for your investment.
Thank you for joining me on this deep dive into the world of turntable bearings and slewing rings. By applying this knowledge, you are better equipped to make informed decisions that will benefit your operations for years to come.