What is a Ring Bearing?
2024-08-20
Understanding Ring Bearings
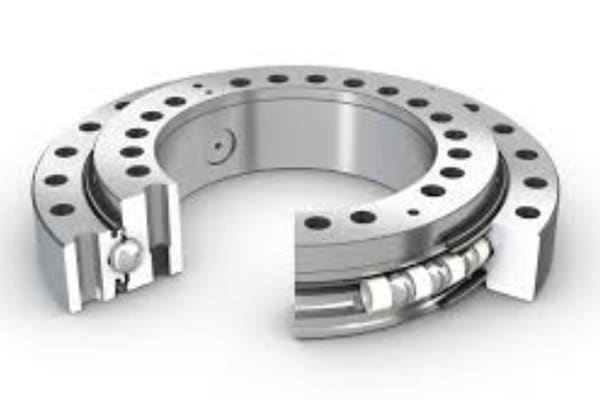
A ring bearing, also known as a slewing bearing or rotary bearing, is a crucial mechanical component designed to support rotational movement around a single axis. It’s an essential part of machinery that requires precise rotation, from heavy construction equipment to advanced medical devices. These bearings are the backbone of various machines, ensuring smooth operation and robust performance.
How Does a Ring Bearing Work?
Ring bearings typically consist of an outer ring, an inner ring, rolling elements (like balls or rollers), and a cage. The rolling elements facilitate smooth rotation by rolling between the inner and outer rings, reducing friction. When a force is applied, the bearing supports the load and allows the connected components to rotate smoothly.
Key Components and Their Functions:
- Outer Ring: The stationary part that is often attached to the machine’s frame.
- Inner Ring: The rotating part that is attached to the rotating component of the machine.
- Rolling Elements: Balls or rollers that reduce friction and support the load.
- Cage: A separator that keeps the rolling elements evenly spaced and prevents them from coming into contact with each other.
Types of Ring Bearings
Ring bearings come in various types, each designed for specific applications and load conditions. Common types include:
- Ball Bearings: These bearings use spherical balls as rolling elements and are suitable for lighter loads and high-speed applications.
- Roller Bearings: Roller bearings use cylindrical rollers as rolling elements and are better suited for heavier loads and lower speeds.
- Tapered Roller Bearings: These bearings have conical rollers and can handle both radial and axial loads.
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings: These bearings use cylindrical rollers and are designed to handle heavy radial loads.
Applications of Ring Bearings
Ring bearings are used in a wide range of industries and applications, including:
- Construction Equipment: Cranes, excavators, and drilling rigs rely on ring bearings for their rotating mechanisms.
- Wind Turbines: Ring bearings support the rotation of the nacelle and rotor.
- Marine Industry: Ship turrets, cranes, and stabilizers use ring bearings.
- Industrial Machinery: Conveyors, mixers, and rotary kilns utilize ring bearings.
- Aerospace: Aircraft landing gear and satellite antennas employ ring bearings.
- Renewable Energy: Solar tracking systems and tidal turbines use ring bearings.
Advantages of Ring Bearings
- High Load Capacity: Ring bearings can handle heavy radial and axial loads.
- Smooth Rotation: The rolling elements ensure smooth and precise rotation.
- Low Friction: Ring bearings reduce friction, increasing efficiency and reducing wear.
- Long Service Life: With proper maintenance, ring bearings can have a long service life.
- Versatility: Ring bearings are available in various sizes and configurations to suit different applications.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Ring Bearing
- Load Capacity: The bearing must be able to support the expected load.
- Operating Speed: The bearing’s speed rating should match the application.
- Operating Environment: Factors like temperature, humidity, and contamination affect bearing life.
- Space Constraints: The bearing’s dimensions must fit within the available space.
- Cost: The cost of the bearing should be considered along with its performance.
Maintenance of Ring Bearings
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the long life and performance of ring bearings. This includes:
- Regular Inspection: Check for signs of wear, damage, or contamination.
- Lubrication: Use the recommended lubricant and follow the lubrication schedule.
- Alignment: Ensure proper alignment to prevent premature wear.
- Avoid Overloading: Avoid overloading the bearing beyond its rated capacity.
In conclusion, ring bearings are indispensable components in many industrial applications, providing smooth and reliable rotational movement. Understanding their types, applications, and maintenance requirements is crucial for selecting the right bearing for a specific application. By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your machinery.