What is a Slewing Gear?
2024-07-29
In the world of heavy machinery and industrial applications, slewing gears play a crucial role in facilitating rotational movement. One of the most common types is the geared slewing ring, which is essential in various equipment ranging from cranes and excavators to wind turbines and aerial platforms. This article explores the definition, components, and applications of slewing gears, with a focus on the importance of geared slewing rings.
Definition and Function
A slewing gear, also known as a slewing bearing or slewing ring, is a rotational rolling-element bearing that supports heavy but slow-turning or slow-oscillating loads. These loads can be either axial (parallel to the axis of rotation) or radial (perpendicular to the axis of rotation). The primary function of a slewing gear is to provide smooth rotational movement and support structural loads.
Geared Slewing Rings
A geared slewing ring is a specific type of slewing bearing that incorporates gears either on the inner or outer race. This integration allows the slewing ring to be directly driven by a pinion or other gear system, facilitating the rotational movement of the machinery it is mounted on. The gear teeth can be straight (spur gears) or helical, each offering different advantages in terms of load capacity and smoothness of operation.
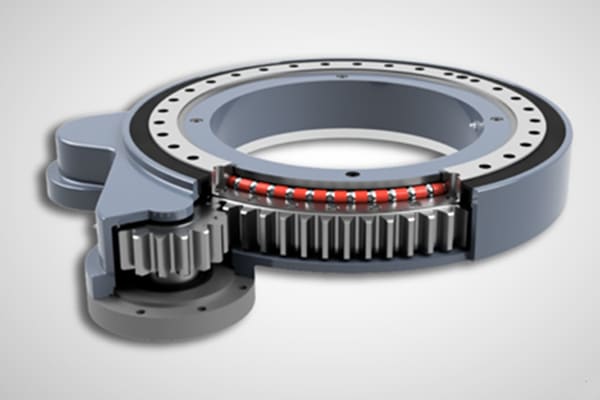

Components of a Slewing Gear
- Inner and Outer Rings: These form the main structure of the slewing ring, containing the raceways for the rolling elements. One of these rings usually features an integrated gear.
- Rolling Elements: These are typically balls or rollers that facilitate smooth rotation by reducing friction between the moving parts.
- Seals: These components protect the internal elements from contamination by dust, debris, and moisture, ensuring longevity and reliable performance.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is critical for reducing friction and wear, thereby extending the operational life of the slewing gear.
Applications of Geared Slewing Rings
- Cranes and Excavators: Geared slewing rings are widely used in cranes and excavators to enable the rotation of the superstructure. This rotation is essential for the maneuverability and precision required in lifting and digging operations.
- Wind Turbines: In wind turbines, slewing gears are used in the yaw mechanism to rotate the nacelle, ensuring that the blades are always aligned with the wind direction for optimal energy capture.
- Aerial Platforms: These gears enable the rotation of the work platform, allowing operators to position themselves accurately for tasks at height.
- Medical Equipment: In medical devices such as CT scanners, slewing rings facilitate the smooth and precise rotation of the imaging equipment around the patient.
Advantages of Geared Slewing Rings
- High Load Capacity: Geared slewing rings can support significant axial, radial, and moment loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Compact Design: By integrating the gear with the bearing, the overall design of the machinery can be more compact, saving space and reducing weight.
- Enhanced Precision: The direct engagement of gears provides precise rotational control, which is critical in applications requiring accurate positioning.
Maintenance and Durability
The longevity and performance of geared slewing rings depend on regular maintenance and proper use. This includes periodic lubrication, inspection for wear and damage, and ensuring that the seals are intact to prevent contamination. High-quality materials and precise manufacturing processes also contribute to the durability of these components.
Conclusion
Geared slewing rings are indispensable in various industrial and construction applications due to their ability to support heavy loads and facilitate precise rotational movement. Their integration into machinery like cranes, wind turbines, and medical equipment highlights their versatility and importance. As technology advances, the design and efficiency of slewing gears continue to improve, driving further innovation in the fields that rely on them.