Who Invented Slewing Rings?
2024-10-25
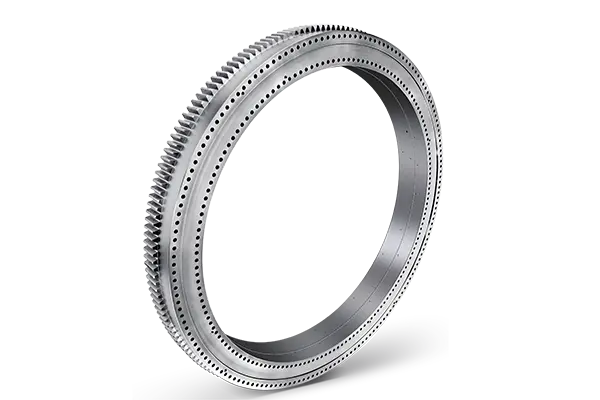
Slewing rings, sometimes referred to as slewing bearings or turntable bearings, are essential components in machinery that require smooth rotational movement under heavy loads. Found in equipment ranging from cranes and excavators to wind turbines and robotics, these components are crucial for both industrial and everyday applications. The concept behind slewing rings evolved through advancements in engineering, with various innovators contributing to the development of these indispensable tools. In this article, we’ll explore the history of slewing rings, the pioneers behind their creation, and how famous slewing rings came to play a pivotal role in modern industry.
Early Beginnings: The Origins of Bearing Technology
The fundamental concept of slewing rings can be traced back to ancient times when humans first devised tools to reduce friction and allow for rotational movement. Early bearing concepts, which eventually led to the development of slewing rings, were employed as far back as Ancient Egypt. For example, in the construction of the pyramids, workers used logs as rollers under heavy stone blocks to facilitate movement. While rudimentary, this principle of reducing friction through rolling action set the stage for the later development of bearing technology.
The Renaissance period saw further progress, with inventor Leonardo da Vinci sketching designs for ball bearings in his manuscripts. His concept of a bearing with balls positioned between two rings demonstrated an early understanding of how friction could be reduced to improve rotational movement. However, these ideas weren’t fully realized until the industrial era.
The Birth of Modern Bearings and Slewing Rings
The invention of the ball bearing is credited to Philip Vaughan, a Welsh inventor, in 1794. Vaughan patented the design for a ball bearing that allowed carts to move more smoothly by placing metal balls between bearing surfaces. This innovation was a turning point in bearing technology, and it eventually led to the creation of specialized bearings like slewing rings.
In the 20th century, the growing demand for heavy machinery in construction, mining, and military applications led to the need for a bearing capable of handling massive loads while providing rotational movement. It was during World War II that slewing rings as we know them today began to take shape. Engineers realized that existing bearings were not sufficient for rotating turrets on tanks, leading to the development of a more robust, large-diameter bearing: the slewing ring.
The Development of Slewing Rings in Modern Industry
The post-war period saw rapid industrial growth, and with it, the rise of specialized manufacturers focused on developing and refining slewing rings. Companies like Rothe Erde (now a part of ThyssenKrupp Bearings), SKF Group, and Kaydon Bearings emerged as leaders in producing famous slewing rings tailored for various heavy-duty applications.
Rothe Erde is credited with pioneering much of the early slewing ring development. Based in Germany, the company specialized in large-diameter bearings that quickly became standard in industries requiring precise, reliable rotational movement. Rothe Erde slewing rings became widely recognized for their durability and ability to handle both axial and radial loads. This breakthrough made slewing rings suitable for large cranes, construction machinery, and even wind turbines.
Contributions of Other Key Manufacturers
Several other companies played essential roles in advancing slewing ring technology, each bringing unique innovations that shaped the industry. SKF, a Swedish company known globally for its bearing expertise, made significant contributions to slewing ring development by improving manufacturing processes and materials. SKF slewing rings are widely used today in renewable energy applications, particularly in wind turbines and solar tracking systems, where durability and precision are crucial.
Kaydon Bearings, now part of the SKF Group, is another name associated with famous slewing rings. Kaydon specializes in custom-engineered, large-diameter bearings used in applications such as aerospace, defense, and medical equipment. The company’s innovations in thin-section and high-load bearings expanded the versatility of slewing rings, allowing them to be used in specialized machinery that requires compact yet powerful rotation mechanisms.
How Slewing Rings Changed Industries
The invention and evolution of slewing rings revolutionized multiple industries. For example, in construction, the ability to rotate the boom of a crane around a stable base allows for efficient material handling and placement, which would be impossible with traditional bearing systems. In renewable energy, slewing rings enable wind turbines to capture optimal wind speeds by adjusting blade angles and orienting the nacelle.
Slewing rings also play a crucial role in transportation and maritime industries. Marine cranes and offshore platforms depend on slewing rings to provide stable, rotational movement under challenging conditions, handling high loads and strong environmental forces.
The Future of Slewing Rings
As industries continue to grow, the demand for slewing rings has expanded, with new materials and advanced manufacturing techniques enabling slewing rings to operate in increasingly challenging environments. Modern slewing rings are often equipped with advanced seals, coatings, and corrosion-resistant materials, ensuring they can withstand extreme weather, high pressures, and abrasive environments.
Manufacturers are also focusing on enhancing the sustainability of slewing rings. SKF, for instance, emphasizes sustainable manufacturing practices and is exploring ways to make slewing rings more energy-efficient. Similarly, companies like IMO Group and Liebherr, known for their robust slewing rings used in cranes and heavy machinery, continue to invest in research and development to enhance the longevity and performance of their products.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Innovation
While it’s difficult to pinpoint a single inventor of the slewing ring, the development of this essential component is the result of contributions from multiple pioneers and manufacturers over centuries. The collaborative efforts of early inventors, industrial engineers, and modern companies like Rothe Erde, SKF, Kaydon, and others have shaped slewing rings into the critical components they are today.
From rotating ancient structures to powering modern-day wind turbines, slewing rings have come a long way. Thanks to ongoing advancements, famous slewing rings continue to support innovation in industries where reliable rotation, strength, and precision are paramount. As technology advances, slewing rings will likely evolve further, continuing to play an indispensable role in industrial and everyday machinery worldwide.